A. Sarangani Province
1. Overall Inflation
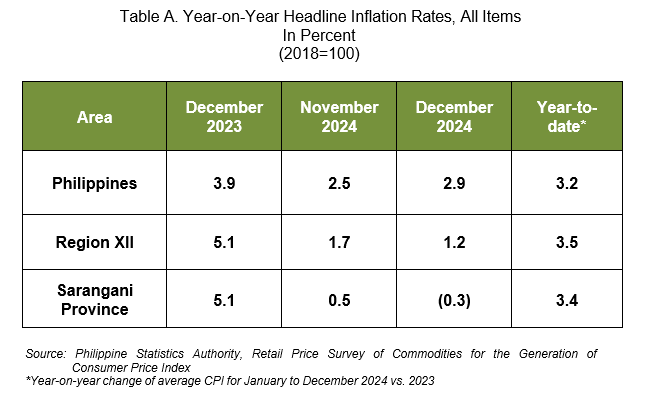
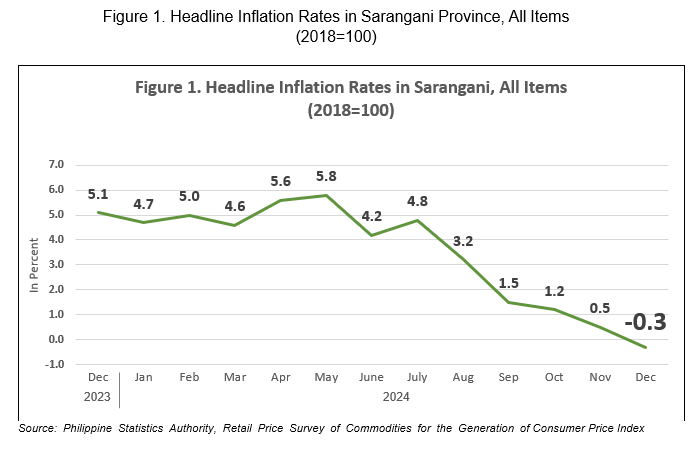
The headline inflation in Sarangani Province posted a decline of 0.3 percent in December 2024 from 0.5 percent in November 2024. In December 2023, the inflation rate was higher at 5.1 percent. (Table A and Figure 1)
1.1 Main Drivers to the Downward Trend of the Overall Inflation (refer to Table B)
The downtrend in the province’s inflation rate in December 2024 was primarily influenced by the slower annual increment in the index of food and non-alcoholic beverages at -2.0 percent from zero inflation in November 2024. This was followed by furnishings, household equipment and routine household maintenance at 0.8 percent in December 2024 from 1.0 percent in the previous month. The index of health also contributed to the downtrend at 1.8 percent during the month from 1.9 percent in November 2024.
On the contrary, the following commodity groups registered higher inflation rates during the month:
a. Alcoholic beverages and tobacco, 3.5 percent from 2.8 percent;
b. Transport, 1.3 percent from -0.2 percent; and
c. Personal care, and miscellaneous goods and services, 4.4 percent from 4.1 percent.
The following are the indices of the commodity groups that retained their previous month’s inflation rates in December 2024:
a. Clothing and footwear, at 1.1 percent;
b. Housing, water, electricity, gas and other fuels at 0.4 percent;
c. Information and communication, at 0.3 percent;
d. Recreation, sport and culture, at 4.7 percent;
e. Education services, at zero inflation;
f. Restaurants and accommodation services, at zero inflation; and
g. Financial services, at zero inflation.
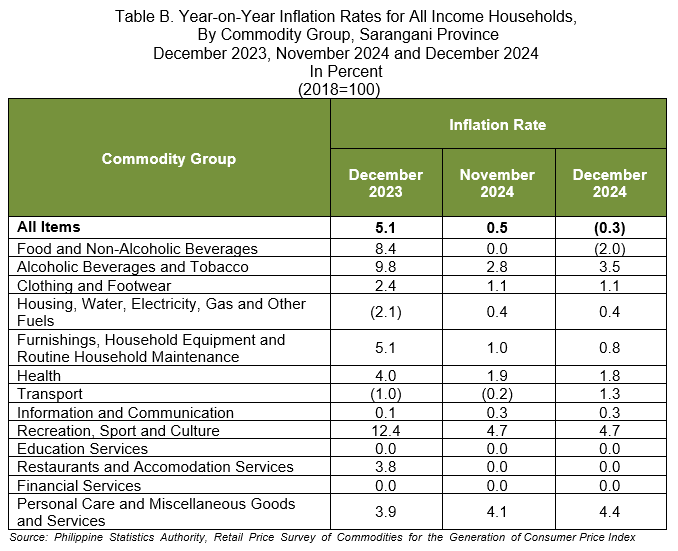
1.2 Main Contributors to the Headline Inflation
The index of food and non-alcoholic beverages contributed to the December 2024 overall inflation for all income households with 275.2 percent share or -0.8 percentage point.
2. Annual Average Inflation
The province's annual average inflation rate for 2024 stood at 3.4 percent, which was lower than the 2023 annual average inflation rate of 6.3 percent.
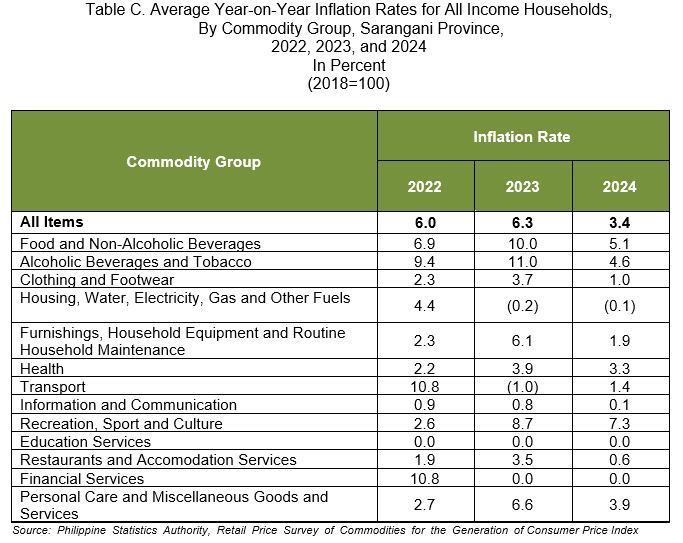
2.1 Main Drivers to the Downward Trend of the 2024 Annual Average Inflation (refer to Table C)
The downtrend in the 2024 annual average inflation at the provincial level was primarily caused by the lower annual average increase in the index of food and non-alcoholic beverages at 5.1 percent in 2024 from 10.0 percent annual average inflation in 2023. This was followed by alcoholic beverages and tobacco at 4.6 percent in 2024 from 11.0 percent annual average inflation in 2023. Restaurants and accommodation services also contributed to the downtrend at 0.6 percent in 2024 from 3.5 percent in 2023.
Slower annual average inflation was also recorded in the indices of the following commodity groups in 2024 compared with 2023:
a. Clothing and footwear, 1.0 percent from 3.7 percent;
b. Furnishings, household equipment and routine household maintenance, 1.9 percent from 6.1 percent;
c. Health, 3.3 percent from 3.9 percent;
d. Information and communication, 0.1 percent from 0.8 percent;
e. Recreation, sport and culture, 7.3 percent from 8.7 percent; and
f. Personal care, and miscellaneous goods and services, 3.9 percent from 6.6 percent.
In contrast, faster annual average inflation was noted in the indices of the following groups in 2024 compared with 2023:
a. Housing, water, electricity, gas and other fuels, -0.1 percent from -0.2 percent; and
b. Transport, 1.4 percent from -1.0 percent.
2.2 Main Contributors to the 2024 Annual Average Inflation
The top three commodity groups contributing to the 2024 annual average inflation were the following:
a. Food and non-alcoholic beverages with 78.6 percent share or 2.7 percentage points;
b. Personal care, and miscellaneous goods and services with 5.9 percent share or 0.2 percentage point; and
c. Alcoholic beverages and tobacco with 4.7 percent share or 0.2 percentage point.
3. Food Inflation
Food inflation at the provincial level further posted a decline of 2.2 percent in December 2024 from -0.2 percent in November 2024. In November 2023, food inflation was higher at 8.7 percent.
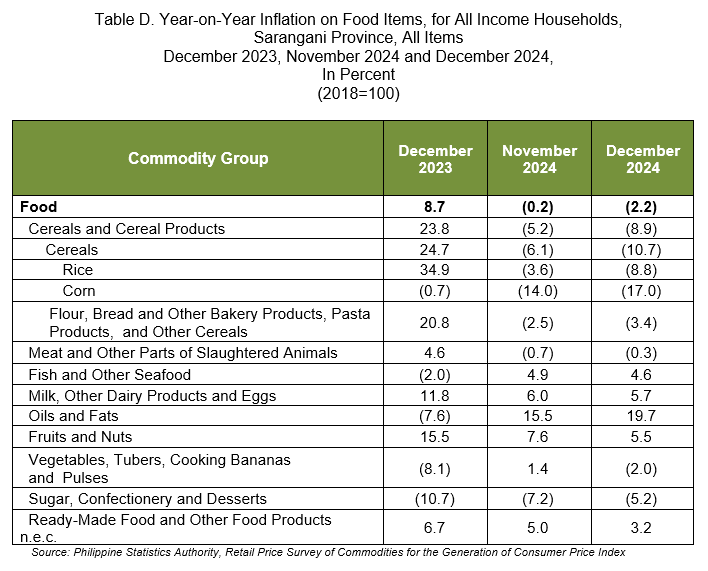
3.1 Main Drivers to the Downward Trend of the Food Inflation (refer to Table D)
The deceleration of food inflation in December 2024 was primarily brought about by the year-on-year decrease in the index of cereals and cereal products, particularly rice at -8.8 percent inflation from a 3.6 percent annual decline in November 2024. This was followed by vegetables, tubers, plantains, cooking bananas and pulses with -2.0 percent during the month from 1.4 percent in November 2024. The index of fruits and nuts also contributed to the downtrend with 5.5 percent during the month from 7.6 percent in November 2024.
Slower annual growth rates during the month were also seen in the following food groups:
a. Fish and other seafood, 4.6 percent from 4.9 percent;
b. Milk, other dairy products, and eggs, 5.7 percent from 6.0 percent; and
c. Ready-made food and other food products n.e.c., 3.2 percent from 5.0 percent.
In contrast, faster annual increments were noted in the indices of the following food groups during the month:
a. Meat and other parts of slaughtered land animals, -0.3 percent from 0.7 percent;
b. Oils and fats, 19.7 percent from 15.5 percent; and
c. Sugar, confectionery and desserts, -5.2 percent from -7.2 percent.
3.2 Main Contributors to the Food Inflation
Food inflation shared 303.8 percent or -0.9 percentage point to the overall inflation in December 2024. The top three food groups in terms of contribution to the food inflation during the month were the following:
a. Cereals and cereal products, which includes rice, corn, flour, bread and other bakery products, pasta products, and other cereals, with 165.7 percent share or -3.7 percentage point;
b. Vegetables, tubers, plantains, cooking bananas and pulses, with 7.8 percent share or -0.2 percentage point; and
c. Sugar, confectionery and desserts, with 6.9 percent share or -0.2 percentage point.
3.3 Annual Average Food Inflation
In 2024, the annual average food inflation rate was observed at 5.3 percent, lower than the recorded annual average food inflation rate of 10.2 percent in 2023.
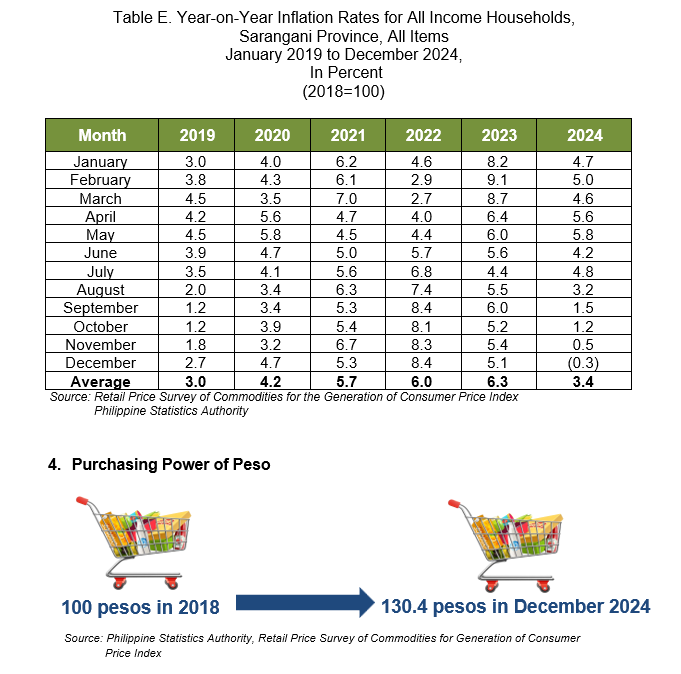
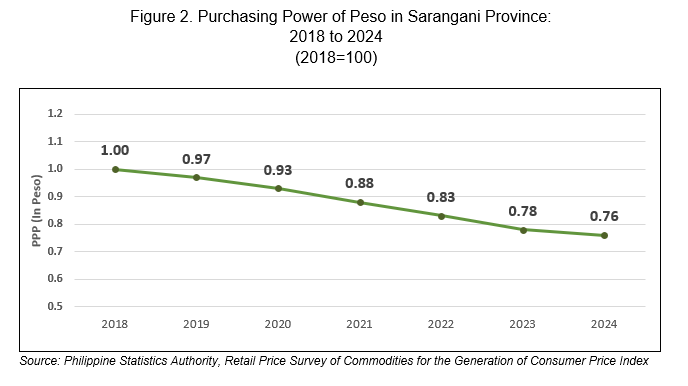
The Purchasing Power of Peso (PPP) in Sarangani Province retained to 0.77 in December 2024. This implies that a peso in 2018 is only worth 77 centavos in December 2024, or you need PhP 130.40 to purchase the same volume of goods and services that cost Php 100.00 in 2018.
The PPP is inversely related to inflation rate. Therefore, as the inflation rate decreases, PPP inclines. In Sarangani Province, PPP has been decreasing on the average of 0.04 annually from 2018 to 2024. By comparison, the PPP in 2024 was 0.76 which implies that the PhP 1.00 in 2018 as the base year, values only Php 0.76 in 2024. (Figure 2)